Osteochondrosis affecting the thoracic spine is often disguised as a pathology of the internal organs. It manifests itself in pain in the heart, shortness of breath, shortness of breath and panic attacks. Therefore, the diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis is more difficult. After detection, conservative treatment is used drugs, physiotherapy, exercise therapy. And in case of severe damage to the thoracic discs and vertebrae, surgery is required.
Brief description of the disease
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine. In the early stages of development, the intervertebral discs are slowly destroyed. They become thin, brittle and form radial cracks on their surfaces. To stabilize the thoracic segment affected by osteochondrosis, the bone tissue of the vertebrae grows with the formation of sharp growths - osteophytes. This leads to a sharp restriction of mobility, constriction of blood vessels and spinal cord.
Pathological degrees
Osteochondrosis degree - a set of symptoms specific to a particular radiographic stage. The more the discs and vertebrae are deformed, the clearer the clinical manifestations. The severity of the pathology always determines the tactics of treatment, you should take into account when choosing drugs and methods of use.
I degree
X-rays do not show any changes at all. However, the intervertebral disc began to collapse due to its inability to retain the moisture needed to repair its tissues. Sometimes there is a little discomfort that quickly disappears after a short rest in the back. Grade 1 osteochondrosis is usually detected accidentally during the diagnosis of other diseases.

Level II
The fibrous ring is empty, fibrous. One of the cracks on the surface of the disc grows, where the nuclear pulposus extends. Radiographs show a decrease in the distance between adjacent vertebral bodies due to a decrease in the height of the disc. Constant compensatory muscle tension results in limited mobility of the chest area and moderate pain.
III degree
The integrity of the annulus fibrosus is compromised, so the pulposus nucleus is compressed. Hernia protrusion occurs - the main cause of severe symptoms and severe complications of thoracic osteochondrosis. The vertebral bodies are deformed, single osteophytes are formed. Chest pain stabilizes, the rate of movement in the spine is significantly reduced.
IV degree
X-ray images clearly show the growth of connective tissue, the formation of numerous osteophytes. Adjacent vertebral bodies are blocked and immobilized. Radicular syndrome develops, often discogenic myelopathy occurs - the spinal cord is compressed, which is dangerous for irreversible consequences. A person finds it difficult to serve himself in daily life and loses the ability to perform professional duties.
Causes of thoracic osteochondrosis
In people over the age of 40-45, thoracic osteochondrosis develops due to the natural aging of the body: slowing of recovery reactions, elasticity, decreased production of collagen, which leads to the strength of ligaments. Occurs at a younger age, as a result of increased stress on the spine or against the background of existing pathologies in the body:
- rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis;
- endocrine and metabolic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, gout, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism;
- Congenital and acquired anomalies, including kyphosis, scoliosis.
Previous spinal injuries, sedentary lifestyle and vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies in the body can lead to early disc destruction.
Characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease

Thoracic osteochondrosis develops gradually without initial manifestation. The danger is in this direction. After a hard day at work, housework or in the garden, a person gets a mild pain and discomfort in the back due to banal muscle fatigue and does not consult a doctor. Therefore, patients are generally diagnosed with a pathology of 2-3 degrees of severity, which is difficult to treat conservatively.
At the beginning
During exacerbation, the pathology may manifest itself as pain that occurs when the body bends and rotates between the shoulder blades. The range of motion is reduced and there are many specific signs of recurrence.
Chest pain
Osteochondrosis is characterized by chest pain. They are not clearly localized and can be given to the hands, clavicle, ribs. The pain in the heart is severe or moderate, similar to angina pectoris, and cannot be relieved by taking nitroglycerin. Sometimes they are similar to the sensations that occur during the exacerbation of cholecystitis, pancreatitis. However, unlike lesions of the pancreas or gallbladder, pain is not accompanied by increased gas production, heartburn, and swelling.
Narrowing in the chest
Pain between the shoulder blades is sometimes accompanied by a feeling of shortness of breath while breathing. A person is expected to be afraid of not understanding the reasons for this situation. Doctors advise not to panic, sit down and measure your heart rate. If the value obtained does not exceed 100 beats per minute, the likelihood of lung or heart damage is extremely low.
Other symptoms
Gradually, the symptoms of osteochondrosis are aggravated by sensitivity disorders. There are numbness, tingling, crawling sensations. From time to time, conditions similar to panic attacks occur. They are characterized by fear, increased heart rate, excessive sweating and cold sweats. If these symptoms are accompanied by chest pain, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin and call a doctor. A number of similar symptoms may indicate a myocardial infarction.
Spinal roots located in the thoracic region innervate the internal organs. Irritation and compression disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Peristalsis is disturbed, epigastric pain, heartburn, belching occur.
Subacute stage signs
After exacerbation, the subacute phase of thoracic osteochondrosis begins. Pain and breathing problems persist, but are less intense. A person is looking for a comfortable position where the pain of the body is not felt for a long time. The duration of the subacute phase is up to two weeks. Following all medical recommendations, remission occurs in the absence of obvious symptoms. Disruption of the regime leads to a new flare-up of osteochondrosis.
Remiss
Mild discomfort may occur during remission or during hypothermia. Acute pain occurs only with osteochondrosis of 2-4 degrees of severity due to very sharp rotation or bending of the body. Exacerbation of chronic pathologies, stress, increased physical activity and prolonged stay in one position of the body can lead to another relapse.
Basics of Diagnosis
The neurologist makes an initial diagnosis based on the patient's complaints and medical history. During the external examination, it detects spots in the chest area with the pressure at which the pain occurs. Functional tests allow to assess the safety of reflexes, to identify sensitivity disorders. Among the instrumental methods, radiography is the most informative. However, for a detailed examination of the spinal segment, CT, MRI can be done. An ECG is prescribed to patients to rule out diseases of the cardiovascular system.
First aid for aggravation
In relapse of thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain is acute, penetrating, so a person should receive first aid. It should be soothed, placed on a hard surface and covered with a warm blanket. If the recurrence is accompanied by increased heart rate, shortness of breath, increased anxiety, then you should call a doctor. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken to relieve pain between the shoulder blades.
How to treat thoracic osteochondrosis
Only an integrated approach to treatment will get rid of all the symptoms of osteochondrosis, slow down or stop the spread to healthy discs and vertebrae. Conservative therapy methods are used with pathology of 1-2 degrees of severity. Osteochondrosis of 3-4 degrees is characterized by the formation of large hernias. Surgical treatment may be required to reduce the pressure on the blood vessels and spinal cord.
Preparations
Drugs of different clinical and pharmacological groups are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis. In the initial stage, agents for parenteral administration have a rapid therapeutic effect. After a few days, the injection solutions are replaced by more reliable tablets, ointments and plasters.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs have a clear analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous effect. Intramuscular application of solutions allows to stop acute pain. Topical application agents are used to relieve mild discomfort between the shoulder blades. And with moderate pain, NSAIDs are good for oral administration.
Muscle relaxant
Muscle relaxants are used to relieve muscle spasms in response to severe pain. Often, treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis begins with intramuscular administration of anesthetic drugs in addition to muscle relaxant tolperizone.
Chondroprotectors
In the case of grade 1 severe pathology, the use of chondroprotectors helps to restore damaged discs. In other cases, they are prescribed to improve metabolism in the affected segment of the spine to prevent the development of the disease.
Preparation of B vitamins
Their use helps to increase blood flow, improve the functioning of the peripheral nervous system, restore trophism and innervation. B vitamins have a beneficial effect on degenerative diseases of the nerves and locomotor system.
Physiotherapy exercises
In case of 1 degree thoracic osteochondrosis, daily exercise therapy allows you to do without the use of drugs. Recovery occurs by strengthening muscles and improving the blood supply to the tissues with food. In other cases, exercise and regular exercise can help prevent healthy spinal segments from interfering with the destructive process and prolong the remission phase.
Permanent complex
The following therapeutic exercises are most effective from a therapeutic point of view when standing:
- Put your palms on your shoulders, bend forward while lifting your bent legs, as if trying to reach the knee with your elbows;
- Raise your left hand, lean to the right. Perform the training in the opposite direction;
- Open your legs shoulder-width apart, raise your arms. Bend forward by touching the opposite foot with the palm.
The number of repetitions is 10-12 times in 2-3 sets.
from a prone position
For these exercises you will need a gym or a thick, double-folded blanket:
- Lie on your stomach, lift your arms and legs at the same time;
- Lie on your back and lift your upper body, extend your palms to your feet;
- Lie on your back, bend one leg, bend the back of the other, try to touch the ground with your knee.
Each exercise should be done 7-10 times.
Don't sit
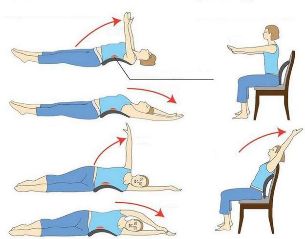
Sharp, high-amplitude movements, including bending, should be avoided when performing such exercises:
- Sit on the floor, lie down, try to touch the opposite foot with your palm;
- Sit in a chair or stool, stretch your arms forward and slowly turn from one side to the other;
- While sitting on the floor, bend your arms at the knees and pull them to your chest as much as possible.
In the first lessons, the exercises should be repeated 5-7 times, and after about a month 15-20 times.
Physiotherapy
Magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF therapy, sinusoidal currents, shock wave therapy, paraffin and ozokerite applications are used to treat thoracic osteochondrosis. In exacerbations, electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, anesthetics, B vitamins, chondroprotectors are performed.
Massage
A massage performed by a specialist helps to relieve pain between the shoulder blades and relax spasmodic skeletal muscles.
For osteochondrosis, any massage is therapeutically effective - classic, vacuum, acupuncture, connective tissue. Self-massage at home is easily done using a wooden or electric long-hand massage.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a method of treating pathology by inserting needles into bioactive points in the human body. They are thin and short, so sometimes there is only a slight discomfort when piercing the skin. However, this effect is also sufficient for the production of substances in the body that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Nutrition
Nutritionists advise patients with osteochondrosis of the chest to avoid fatty meats, rich soups, smoked meats, home and factory marinades. It is necessary to limit the amount of salt in the diet, which causes edema. Every day you should drink about 2. 5 liters of fluid - water, vegetable juices, berry drinks, fruit compotes.
Folk remedies
Herbs, ointments, alcohol and oil rubs, compresses, are allowed to be used by neurologists after the main therapy. Folk remedies are used to relieve mild pain between the shoulder blades, sometimes after physical exertion.
Celery Root
Peel a large celery root, chop finely and squeeze the juice. Add 100 g chopped fresh celery. Take 3 tablespoons 4 times a day with meals to clean the vertebral structures from harmful salt deposits.
Sunflower root
Pour a teaspoon of dry crushed sunflower roots in a glass of warm water. Bring to a boil, simmer for 20 minutes on low heat, cool under the lid, drain. Drink 3-4 times a day.
Home ointment

In a solution, add a tablespoon of gum turpentine and thick honey, add 2 drops of juniper, rosemary, eucalyptus essential oils. Inject 100 g of medical oil gel into small portions. Mix, transfer to a jar, keep in the refrigerator, rub on the back of the pain.
During pregnancy
Many systemic analgesics are contraindicated during pregnancy, so neurologists prefer drugs for external use - ointments, gels, patches. If you can't do without taking the pill, the doses are significantly reduced. The main therapies for osteochondrosis of the chest during childbirth are massage and sports therapy.
Possible results
In the absence of medical intervention, thoracic osteochondrosis can lead to pneumosclerosis, arrhythmias, vegetative-vascular dystonia, deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract, sexual and reproductive dysfunction in women and men.Prevention and prognosis
Prognosis is favorable with timely detection of the disease, competent, comprehensive treatment. If complications of thoracic osteochondrosis develop, only compliance with all medical recommendations will allow you to achieve a stable remission.
As a prevention of pathology, neurologists recommend removing the factors that provoke it from a normal lifestyle. These include overweight, low physical activity, vitamin and mineral deficiencies, and excessive stress on the spine.












































